What is a solar greenhouse?
It’s a structure with a translucent cover that captures all the sun’s energy and light, allowing us to protect our crops from adverse weather conditions, such as rain, cold weather and strong winds.
By creating a microclimate, we manage to increase the production of our fruit and vegetable crops no matter what time of year it is, without resorting to the use of fossil fuels or sacrificing the quality and taste of our produce.
This way, we generate higher productivity at a very competitive price, favouring a circular economy through optimal management of scarce resources such as as water, and by reusing and recycling the largest possible number of the elements involved in the production process.



This is achieved by combining traditional agricultural techniques of the region with technology and continuously incorporating innovations, to improve the productivity, quality and sustainability of the crops, including:
- The use of sanding, plastic covers and drip irrigation systems to create a microclimate, increase productivity and reduce the consumption of resources.
- The use of biological pest control to produce healthy and tasty fruit and vegetables.
- The use of seed varieties that are adapted to the conditions of the region and the needs of the consumer.
LOCATION


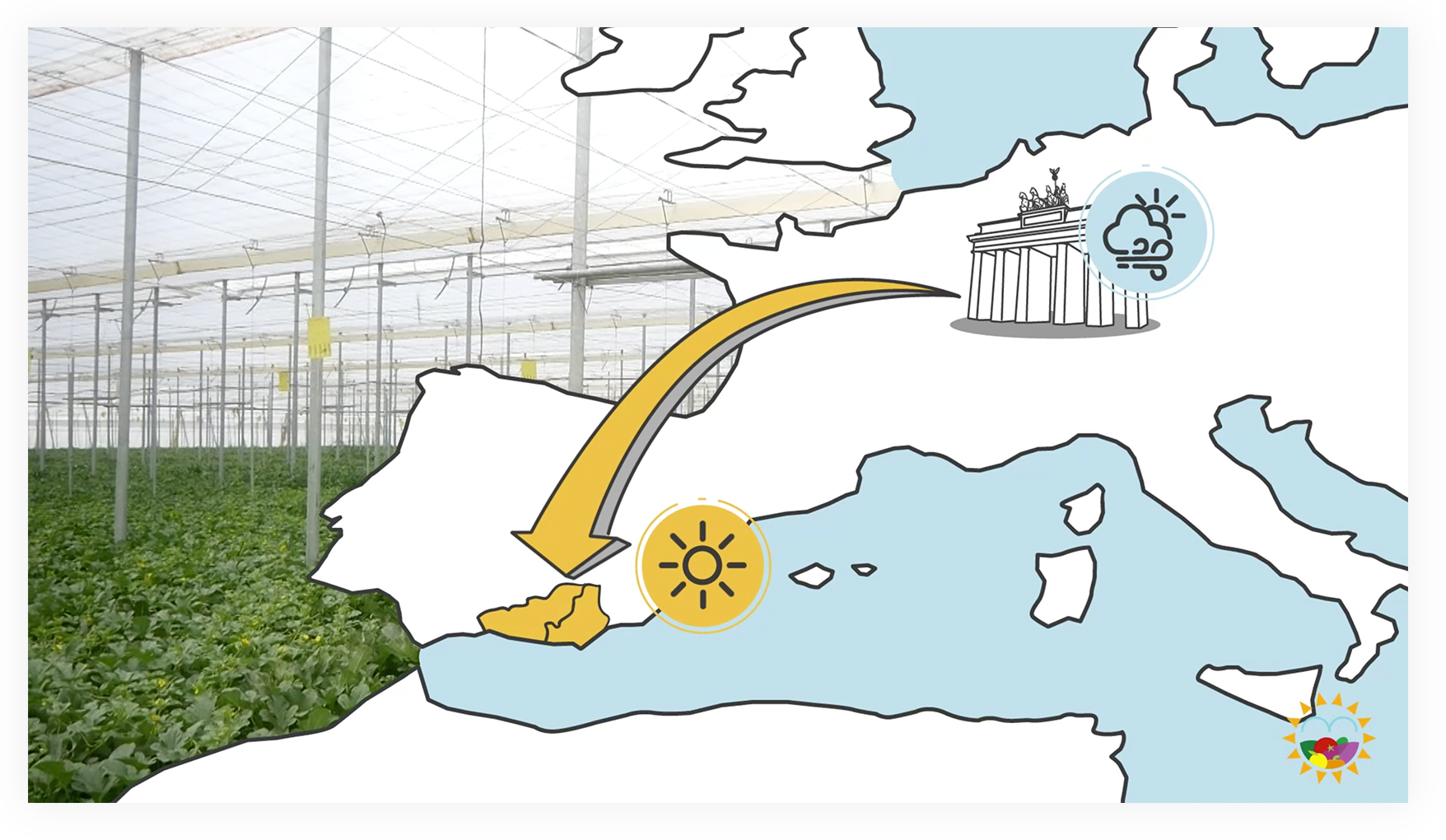
Our work in solar greenhouses takes place in Europe, particularly in the south of the continent, such as the Andalusian regions of Almería and the coast of Granada.
In fact, around 25% of all the fruit and vegetables that Europe needs are produced in these regions. That’s enough to feed more than 500 million European citizens for 9 months a year.

SOCIOECONOMIC CONTRIBUTION

The production model of solar greenhouses in southern Europe is based on the idea of the small farmer and local families, thereby contributing to local economic development in the regions where solar greenhouses are located.

The more than 30,000 hectares of land covered in plastic are distributed among 12,500 farms and families, resulting in low ownership concentration and encouraging GDP growth and the emergence and development of related industries, such as transportation.

We also promote the importance of the role of immigrant workers and women in the European agricultural sector:
- Women represent 71% of employment in marketing companies and 30% in the field.
- Immigrant workers now account for 65% of all personnel.
- More than 90% of farmers in the region have formal training.

HOW THE SYSTEM WORKS


We’re talking about the development of a social economy trading system, specifically cooperatives, traditional markets known locally as “alhóndigas”, and Agrarian Transformation Societies (SATs). This system helps improve the position of the farmer in the supply chain, it provides them with access to technical advice and financing, and allows for the incorporation of new technologies, in what is a great example of social cooperation that benefits the region as a whole.

The European agricultural sector complies with strict controls and standards when it comes to the production processes of crops in solar greenhouses, as well as the transportation, distribution and marketing of food, both in Europe and around the world.

The production process is characterised by its sustainable and environmentally-friendly practices, which actively contribute to combating climate change and the scarcity of natural resources. These practices also promote local development, particularly among families, which restricts oligopolies, and they promote healthy food independence across Europe.
POSITIVE EFFECTS
Solar greenhouse agriculture has not only
managed to increase productivity in the sector,
it also contributes to local development and
consumer welfare in several key ways.
Solar greenhouse agriculture has not only managed to increase productivity in the sector, it also contributes to local development and consumer welfare in several key ways.
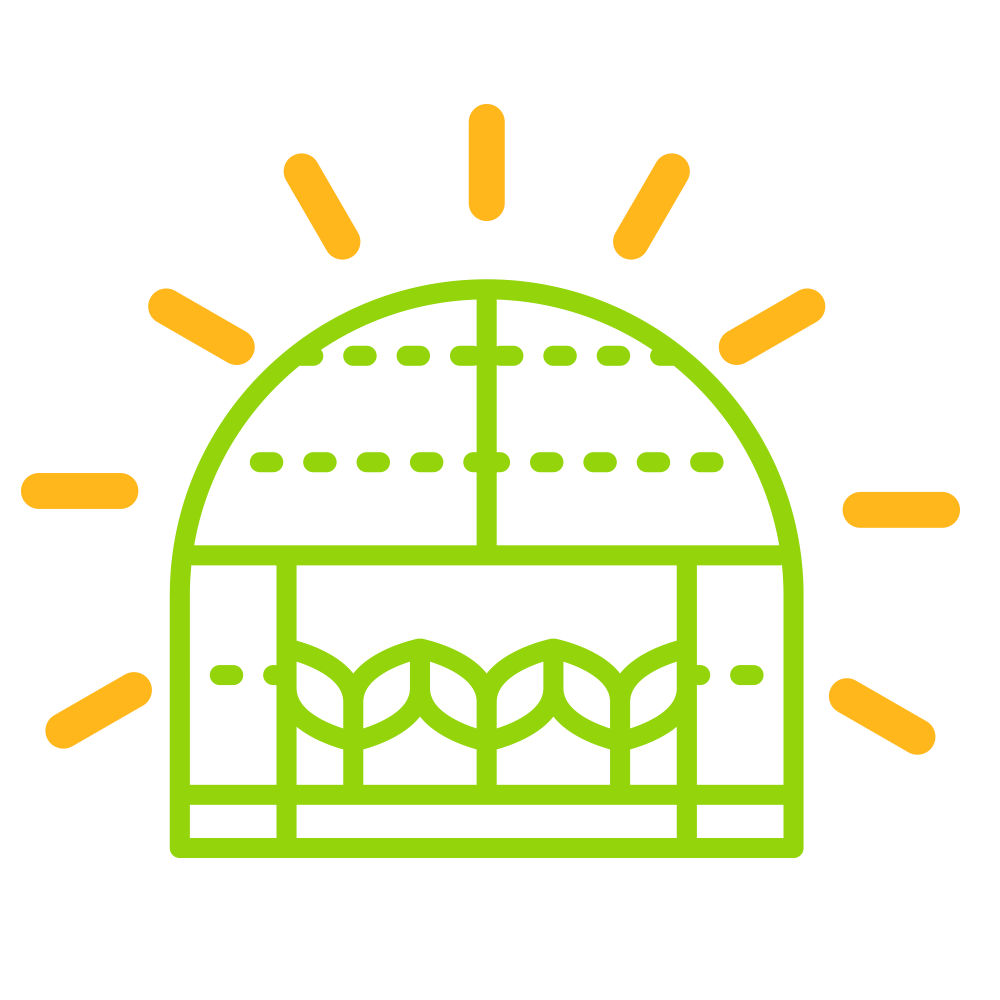
Sustainability:
We care about maintaining a negligible water footprint, thereby conserving water which is such a scarce natural resource.
Solar greenhouses also help cool the planet and reduce C02 emissions, functioning as active agents in the fight against global warming.
People:
We contribute to local development and our team is becoming increasingly qualified: 91% of solar greenhouse farmers have some kind of official formal training and the Good Agricultural Practices certification.
It’s also worth highlighting the fundamental role immigrant workers play in solar greenhouses and the success of their integration; they represent 65% of all hires in the sector. The work of women is also noteworthy, and they contribute to normalising equality and social justice in the industry.

Food quality and safety:
We comply with all quality and safety standards backed by European examinations and regulations regarding production, marketing and distribution processes. The same is true of the monitoring of all our produce, which is based on a system of traceability and allows us to find out the life cycle of our products, from the moment we plant the crop, until the moment you buy the produce.

Health and nutrition:
We seek to promote healthy eating habits, especially among little ones. Through educational programs we teach them that the consumption of fruit and vegetables, together with physical exercise, is the basis of a good diet and a healthy life.
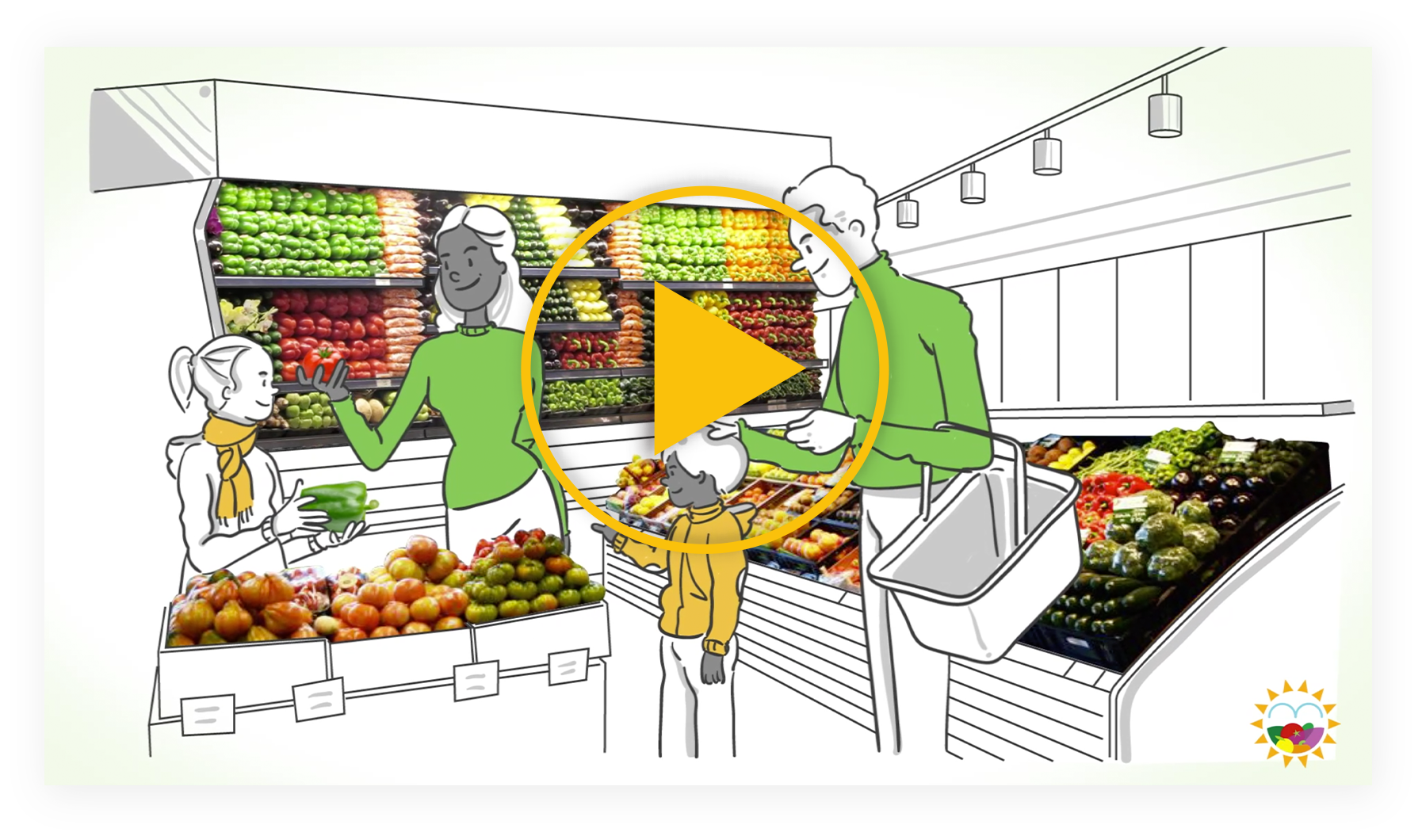
VIDEO
Discover all you need to know about solar greenhouses in southern Europe,
especially regarding key aspects such as sustainability and environmental protection,
and the safety, quality and traceability of our crops.
Discover all you need to know about solar greenhouses in southern Europe, especially regarding key aspects such as sustainability and environmental protection, and the safety, quality and traceability of our crops.